1. Introduction
InfiniBand (IB) is a high-speed, low-latency interconnect technology widely used in High-Performance Computing (HPC), Artificial Intelligence (AI) clusters, cloud data centers, and large-scale simulations. Its extreme bandwidth and ultra-low latency make it the preferred choice for workloads requiring massive parallel computing and rapid data exchange. The proliferation of large-scale AI models, such as GPT, has fueled a rapid growth in demand for InfiniBand, as industry leaders like NVIDIA rely on it for training massive systems.
2. Development Overview
InfiniBand, short for "infinite bandwidth," was created to overcome the limitations of the PCI bus in the 1990s. It introduced Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA), which enables faster and more efficient communication between systems. The InfiniBand Trade Association (IBTA) released the first specification in 2000, and the technology has since evolved through generations, reaching speeds up to 400Gb/s with NDR and beyond.
3. Core Technology and Architecture
3.1 RDMA Core Technology
Unlike traditional TCP/IP networking, which requires multiple copies of data through system memory, RDMA allows the network adapter of one system to directly access the memory of another. This reduces CPU overhead and transmission latency to the sub-microsecond level while improving overall efficiency.
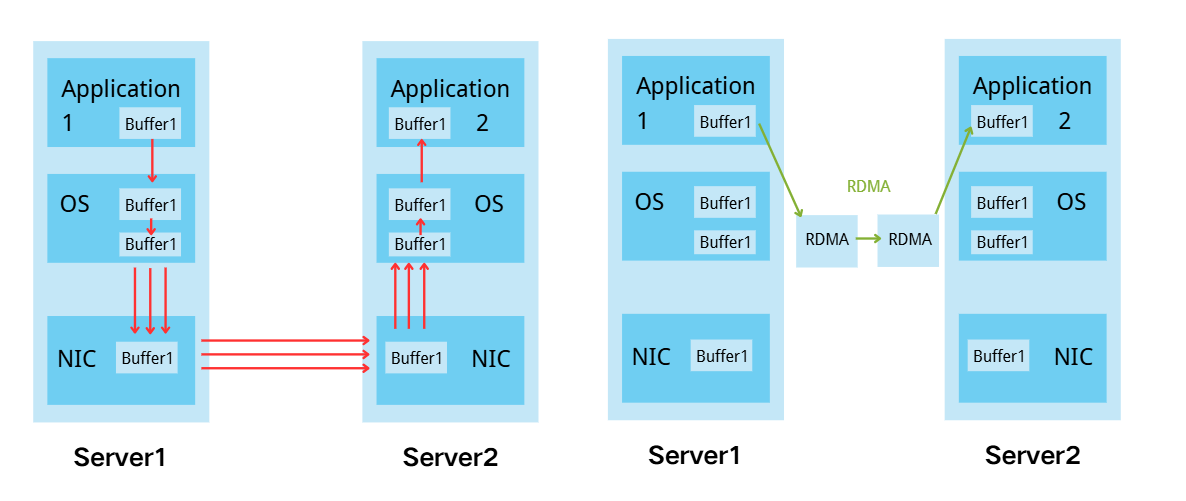
3.2 The Network Architecture of InfiniBand
The schematic diagram of the network topology of InfiniBand is as follows:
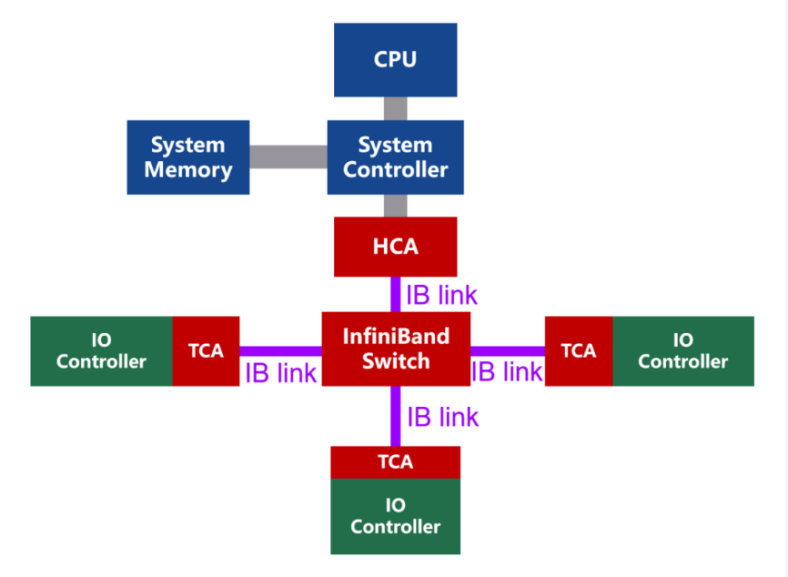
InfiniBand uses a channel-based architecture consisting of:
- HCA (Host Channel Adapter): Connects servers, GPUs, or storage systems to the IB fabric via PCIe.
- TCA (Target Channel Adapter): Provides connectivity for storage and other targets.
- Switches & Routers: Direct traffic and connect subnets.
- Links: Copper or optical cables enabling high-speed connections.
Each subnet can support up to 60,000 nodes, with switches performing ultra-low latency forwarding (under 100ns). Cut-through switching and efficient routing make IB significantly faster than Ethernet in HPC/AI workloads.
4. Core Components of an InfiniBand Network
4.1 Host Channel Adapters (HCAs)
HCAs connect servers to the InfiniBand fabric, delivering high throughput and low latency. They support speeds from HDR to NDR and enable GPU Direct for optimized data movement.
- Function: Connects servers, GPUs, or storage systems to the IB fabric via PCIe interface.
- Key Features: Supports RDMA, GPU Direct, and multi-protocol operations.
Example Models:

- NVIDIA ConnectX-7
- 400G InfiniBand PCIe Gen5
- Programmable Datapath In-Network Computing
4.2 InfiniBand Switches
Switches form the backbone of IB networks, aggregating bandwidth and enabling flexible topologies with varying port counts for scale-out performance.
- Function: Core of IB fabric interconnection, directing traffic between nodes.
- Topology Support: Fat Tree, Dragonfly, Torus, and custom designs.
Example Models:

- Quantum-2 Switch
- 64-ports 400G InfiniBand
- 128-ports 200G
- In-Network Computing
4.3 Cables & Transceivers
Includes Active Optical Cables (AOCs), Direct Attach Cables (DACs), and optical transceivers to enable both short and long-reach connectivity.
Types:
- DAC (Direct Attach Copper): Short distance, cost-effective
- AOC (Active Optical Cable): Longer distances, low signal loss
- Optical transceivers: (e.g., QSFP56)
Speeds: HDR (200Gb/s), NDR (400Gb/s)
5. Key Advantages
- Performance: Port speeds up to 400Gb/s and latency as low as 100–150ns, far outperforming Ethernet.
- Efficiency: Offloads networking from CPUs, reducing utilization and power consumption.
- Parallel Workload Optimization: GPU Direct RDMA and adaptive routing ensure near-linear scaling for large clusters.
- Lower TCO: Higher performance per watt and per rack reduce total costs despite higher upfront investment.
6. Application Scenarios
- HPC: Weather forecasting, molecular dynamics, scientific simulations.
- AI Training: Large-scale deep learning clusters for LLM and CV models.
- Financial Services: High-Frequency Trading (HFT) environments.
- Big Data Analytics: Real-time data processing and analysis.
7. Canopy Wave's Solution
Canopy Wave delivers end-to-end InfiniBand solutions, covering hardware sourcing, network design, configuration, and integration. Our global supply chain and proven expertise help clients in HPC and AI achieve faster deployment, enhanced reliability, and optimized costs.
8. Conclusion
InfiniBand offers unmatched performance, scalability, and efficiency for HPC, AI, and other demanding workloads.